Radio
The <Radio> and <Radio.Group> components allow users to select one option from a set of options. They are useful for presenting a list of options to users and collecting their responses.
The <Radio.Group> not only groups the radio buttons but also manages their state. This means you can easily control which option is selected by default and dynamically update the selection based on user interactions.
Anatomy
The radio button component is comprised of a set of clickable circles (the inputs) with text labels positioned to the right. If there is a group of radio buttons, a group label can be added.

- Group label: Describes the group of options or provides guidance for making a selection.
- Radio button input: Indicates the state of a radio button. By default, no option will be preselected.
- Radio button label: Describes the information you want to select or unselect.
Appearance
The appearance of a component can be customized using the variant and size props. These props adjust the visual style and dimensions of the component, available values are based on the active theme.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
variant | - | The available variants of this component. |
size | - | The available sizes of this component. |
Usage
Radio buttons are used for mutually exclusive choices, where only one option can be selected at a time. They are ideal when you want the user to choose a single option from a small list of predefined choices. When a user selects a new option, the previous choice is automatically deselected.
The <Radio> should never be used alone because radio buttons are designed for selecting one option from multiple mutually exclusive choices. For that the <Radio.Group> should be wrapped around the <Radio>. If you want one option you could use the <Checkbox> instead.
Overflow content
We recommend radio button labels being fewer than three words because shorter radio button labels improve readability and reduce cognitive load, making it easier for users to quickly understand and select options. This enhances the overall user experience, especially on small screens.
If you are tight on space, consider rewording the label. Do not truncate radio button label text with an ellipsis.
Long labels may wrap to a second line, and this is preferable to truncation. Text should wrap beneath the radio button.

If the label is long, wrap to a second line.

Do not truncate radio button label text with an ellipsis.
Number of options
Radio groups are most effective with a small set of choices that can be taken in at a glance. Once the list grows to around five or more options, scanning becomes slower and the vertical space required increases. If the number of options falls into a moderate range, roughly five to fifteen, use the select component instead to keep the interface compact and maintain scanning efficiency.
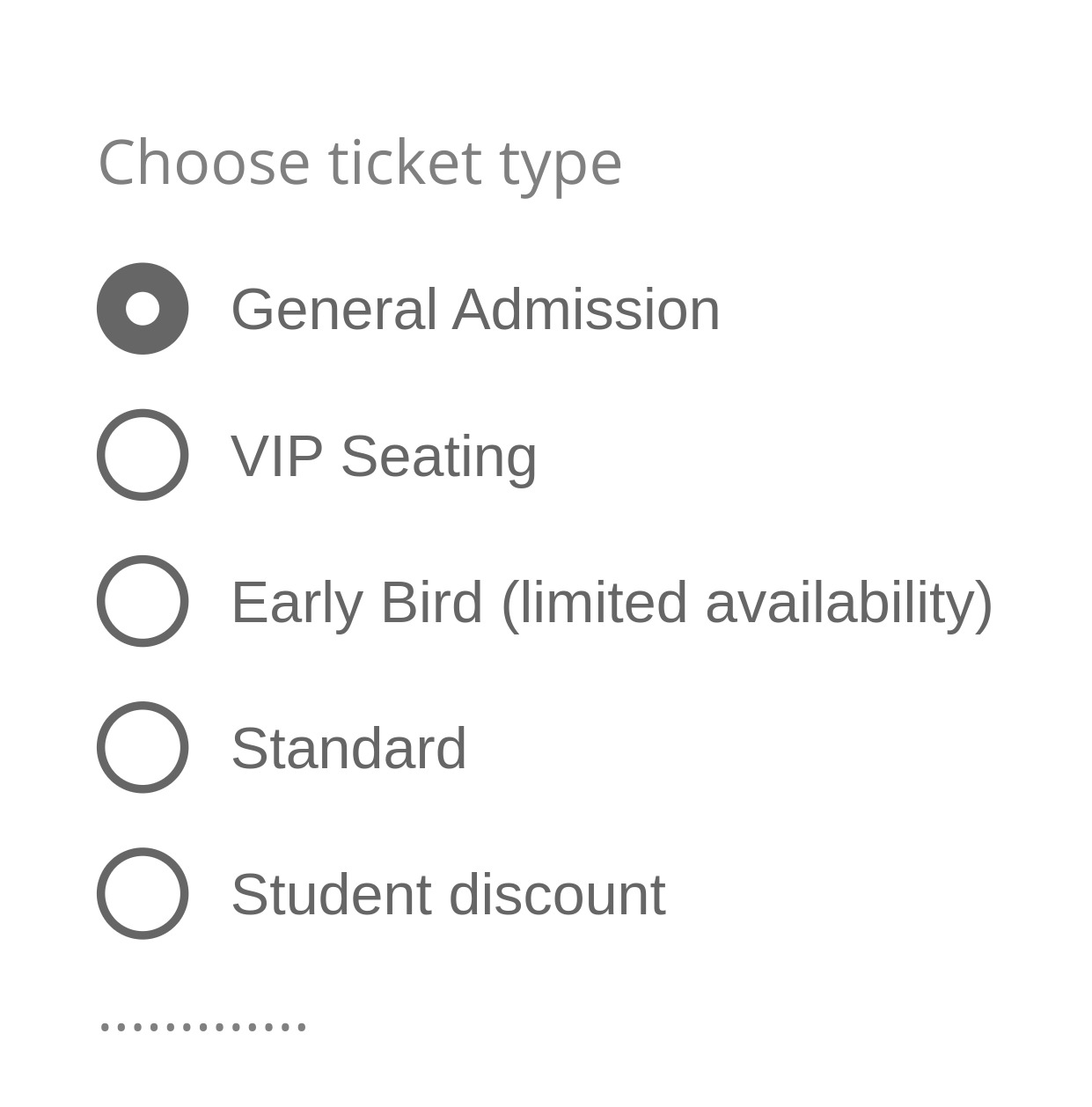
When a radio group is long enough to create clutter, overload, or excessive scrolling, keep it compact while ensuring all options remain accessible. Present only the most relevant five to eight choices initially, with the rest hidden until revealed. Apply this approach sparingly when all options can be scanned easily without causing frustration.
If the selected value is within the collapsed section, the component renders in its expanded state by default.
Ordering of Options
Options should be arranged by relevance to help users find what they need quickly. Prioritizing by factors such as frequency of use, overall popularity, or recency of interaction ensures the most useful items appear first. Alphabetical order should be considered only when no meaningful ranking criteria are available, as it may not align with user priorities or usage patterns.
Single vs. multiple selection
Use radio buttons when users must choose only one option from a group. For example, selecting a payment method like Credit Card, PayPal, or Invoice, or picking a seat category such as Balcony, Orchestra, or Standing.
Radio buttons are best when the options are mutually exclusive, the user is required to make a choice, and the number of options is limited and visible. If users can select more than one option, use checkboxes instead, such as when subscribing to event categories (Concerts, Theater, Sports) or enabling account notifications (Email, SMS, App), where each option is independent.
Use radio buttons when only one option can be selected.
Use checkboxes when more than one option can be selected.
Props
Radio
aria-describedby?string;
aria-details?string;
aria-label?string;
aria-labelledby?string;
autoFocus?boolean;
children?ReactNode;
dir?string;
disabled?boolean;
"false"hidden?boolean;
id?string;
inert?boolean;
inputRef?RefObject<HTMLInputElement | null>;
lang?string;
onAnimationEnd?AnimationEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onAnimationEndCapture?AnimationEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onAnimationIteration?AnimationEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onAnimationIterationCapture?AnimationEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onAnimationStart?AnimationEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onAnimationStartCapture?AnimationEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onAuxClick?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onAuxClickCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onBlur?(e: FocusEvent<Element, Element>) => void;
onClick?(e: MouseEvent<FocusableElement, MouseEvent>) => void;
onPress instead. onClick is an alias for onPress
provided for compatibility with other libraries. onPress provides
additional event details for non-mouse interactions.onClickCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onContextMenu?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onContextMenuCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onDoubleClick?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onDoubleClickCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onFocus?(e: FocusEvent<Element, Element>) => void;
onFocusChange?(isFocused: boolean) => void;
onGotPointerCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onGotPointerCaptureCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onHoverChange?(isHovering: boolean) => void;
onHoverEnd?(e: HoverEvent) => void;
onHoverStart?(e: HoverEvent) => void;
onKeyDown?(e: KeyboardEvent) => void;
onKeyUp?(e: KeyboardEvent) => void;
onLostPointerCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onLostPointerCaptureCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onMouseDown?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onMouseDownCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onMouseEnter?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onMouseLeave?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onMouseMove?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onMouseMoveCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onMouseOut?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onMouseOutCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onMouseOver?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onMouseOverCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onMouseUp?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onMouseUpCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onPointerCancel?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onPointerCancelCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onPointerDown?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onPointerDownCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onPointerEnter?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onPointerLeave?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onPointerMove?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onPointerMoveCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onPointerOut?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onPointerOutCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onPointerOver?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onPointerOverCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onPointerUp?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onPointerUpCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onPress?(e: PressEvent) => void;
onPressChange?(isPressed: boolean) => void;
onPressEnd?(e: PressEvent) => void;
onPressStart?(e: PressEvent) => void;
onPressUp?(e: PressEvent) => void;
onScroll?UIEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onScrollCapture?UIEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onTouchCancel?TouchEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onTouchCancelCapture?TouchEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onTouchEnd?TouchEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onTouchEndCapture?TouchEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onTouchMove?TouchEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onTouchMoveCapture?TouchEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onTouchStart?TouchEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onTouchStartCapture?TouchEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onTransitionCancel?TransitionEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onTransitionCancelCapture?TransitionEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onTransitionEnd?TransitionEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onTransitionEndCapture?TransitionEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onTransitionRun?TransitionEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onTransitionRunCapture?TransitionEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onTransitionStart?TransitionEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onTransitionStartCapture?TransitionEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onWheel?WheelEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
onWheelCapture?WheelEventHandler<HTMLLabelElement>;
ref?Ref<HTMLLabelElement>;
ref.current to null
(or call the ref with null if you passed a callback ref).
@see {@link https://react.dev/learn/referencing-values-with-refs#refs-and-the-dom React Docs}slot?string | null;
null value indicates that the local props completely override all props received from a parent.translate?"yes" | "no";
valuestring;
width?WidthProp;
"full"Radio.Group
aria-describedby?string;
aria-details?string;
aria-errormessage?string;
aria-label?string;
aria-labelledby?string;
children?ReactNode[]collapseAt?number;
"undefined"defaultValue?string | null;
description?string;
"none"dir?string;
disabled?boolean;
true, the radio group is disabled."false"error?boolean;
true, the radio group is considered invalid and if set the errorMessage is shown."false"errorMessage?string;
"none"form?string;
<form> element to associate the input with.
The value of this attribute must be the id of a <form> in the same document.
See MDN.hidden?boolean;
id?string;
inert?boolean;
isReadOnly?boolean;
label?ReactNode;
"none"lang?string;
name?string;
onAnimationEnd?AnimationEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onAnimationEndCapture?AnimationEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onAnimationIteration?AnimationEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onAnimationIterationCapture?AnimationEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onAnimationStart?AnimationEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onAnimationStartCapture?AnimationEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onAuxClick?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onAuxClickCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onBlur?(e: FocusEvent<Element, Element>) => void;
onChange?(value: string) => void;
onClick?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onClickCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onContextMenu?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onContextMenuCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onDoubleClick?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onDoubleClickCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onFocus?(e: FocusEvent<Element, Element>) => void;
onFocusChange?(isFocused: boolean) => void;
onGotPointerCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onGotPointerCaptureCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onLostPointerCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onLostPointerCaptureCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onMouseDown?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onMouseDownCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onMouseEnter?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onMouseLeave?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onMouseMove?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onMouseMoveCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onMouseOut?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onMouseOutCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onMouseOver?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onMouseOverCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onMouseUp?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onMouseUpCapture?MouseEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onPointerCancel?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onPointerCancelCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onPointerDown?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onPointerDownCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onPointerEnter?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onPointerLeave?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onPointerMove?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onPointerMoveCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onPointerOut?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onPointerOutCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onPointerOver?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onPointerOverCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onPointerUp?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onPointerUpCapture?PointerEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onScroll?UIEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onScrollCapture?UIEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onTouchCancel?TouchEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onTouchCancelCapture?TouchEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onTouchEnd?TouchEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onTouchEndCapture?TouchEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onTouchMove?TouchEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onTouchMoveCapture?TouchEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onTouchStart?TouchEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onTouchStartCapture?TouchEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onTransitionCancel?TransitionEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onTransitionCancelCapture?TransitionEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onTransitionEnd?TransitionEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onTransitionEndCapture?TransitionEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onTransitionRun?TransitionEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onTransitionRunCapture?TransitionEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onTransitionStart?TransitionEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onTransitionStartCapture?TransitionEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onWheel?WheelEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
onWheelCapture?WheelEventHandler<HTMLDivElement>;
orientation?AlignmentProp;
"vertical"readOnly?boolean;
"false"required?boolean;
true, the radio group is required."false"slot?string | null;
null value indicates that the local props completely override all props received from a parent.translate?"yes" | "no";
validate?(value: string | null) => true | ValidationError | null;
validationBehavior="native". For realtime validation, use the isInvalid
prop instead.validationBehavior?"native" | "aria";
'native'value?string;
width?WidthProp;
100%Alternative components
Choosing the right alternative to radio buttons is important for providing an optimal user experience, especially when different types of selections are required. Depending on the nature of the choices and the desired interaction, the following components can serve as an alternative to radio buttons:
Select: Ideal when the user needs to choose one option from moderate number of options (e.g., 5-15) to choose from. Unlike radio buttons, which display all options at once, a select component can hide the options until needed, saving space in the UI.